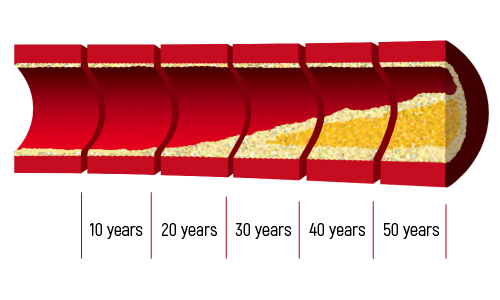
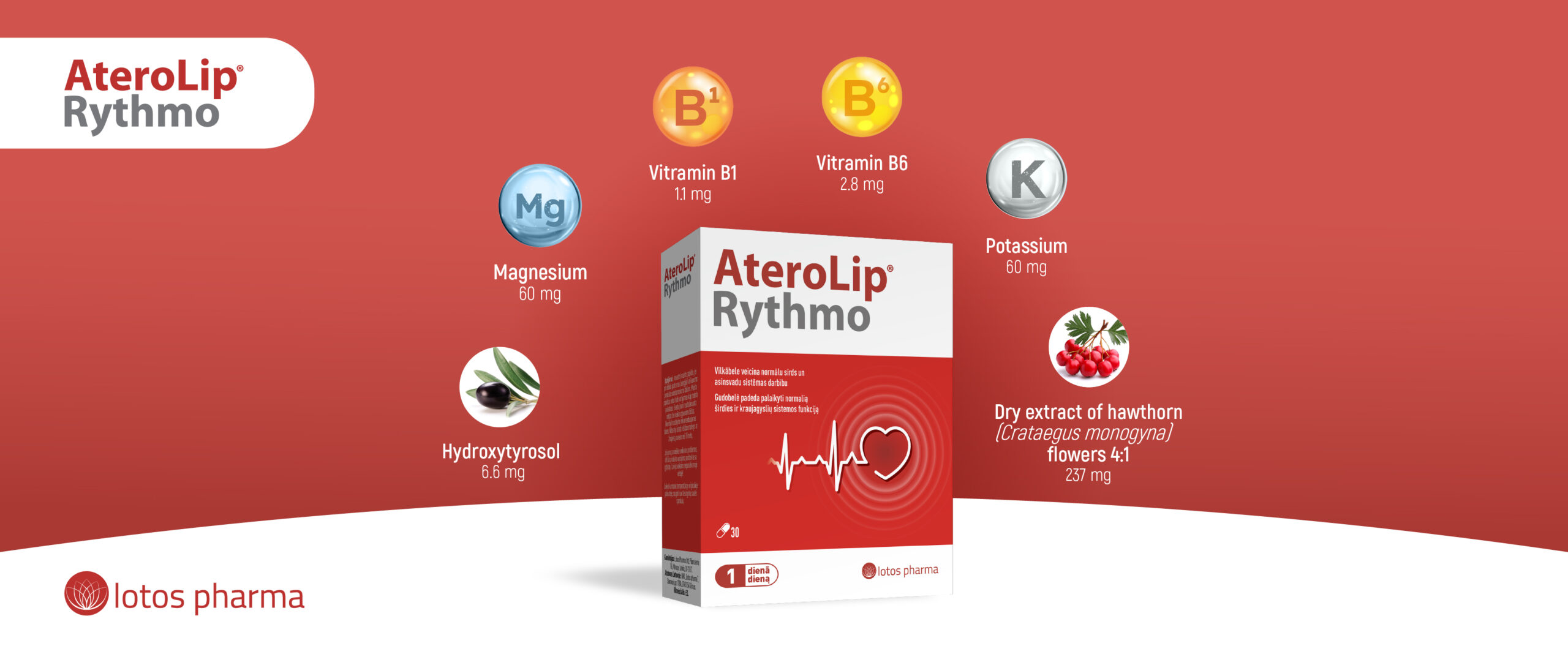
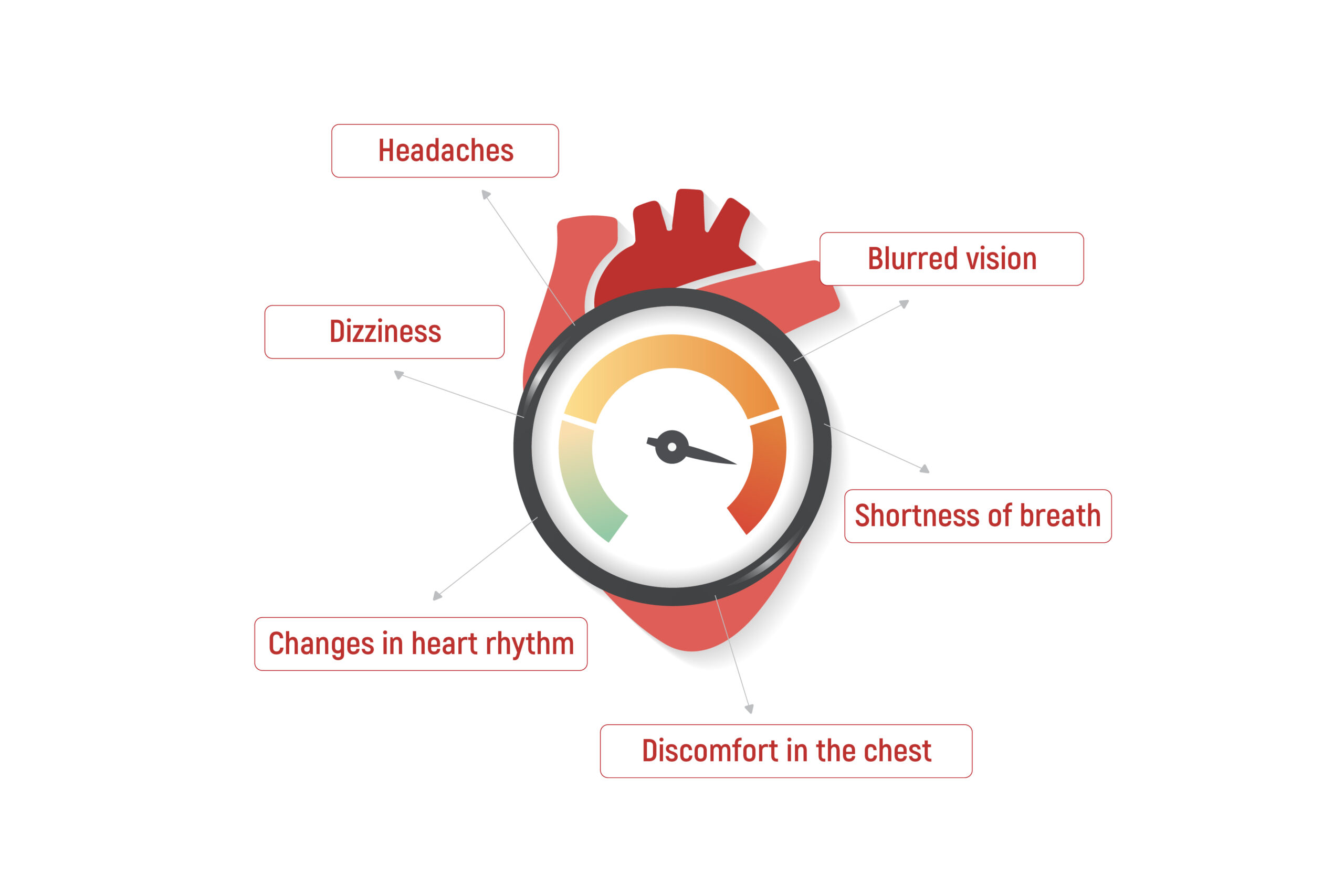
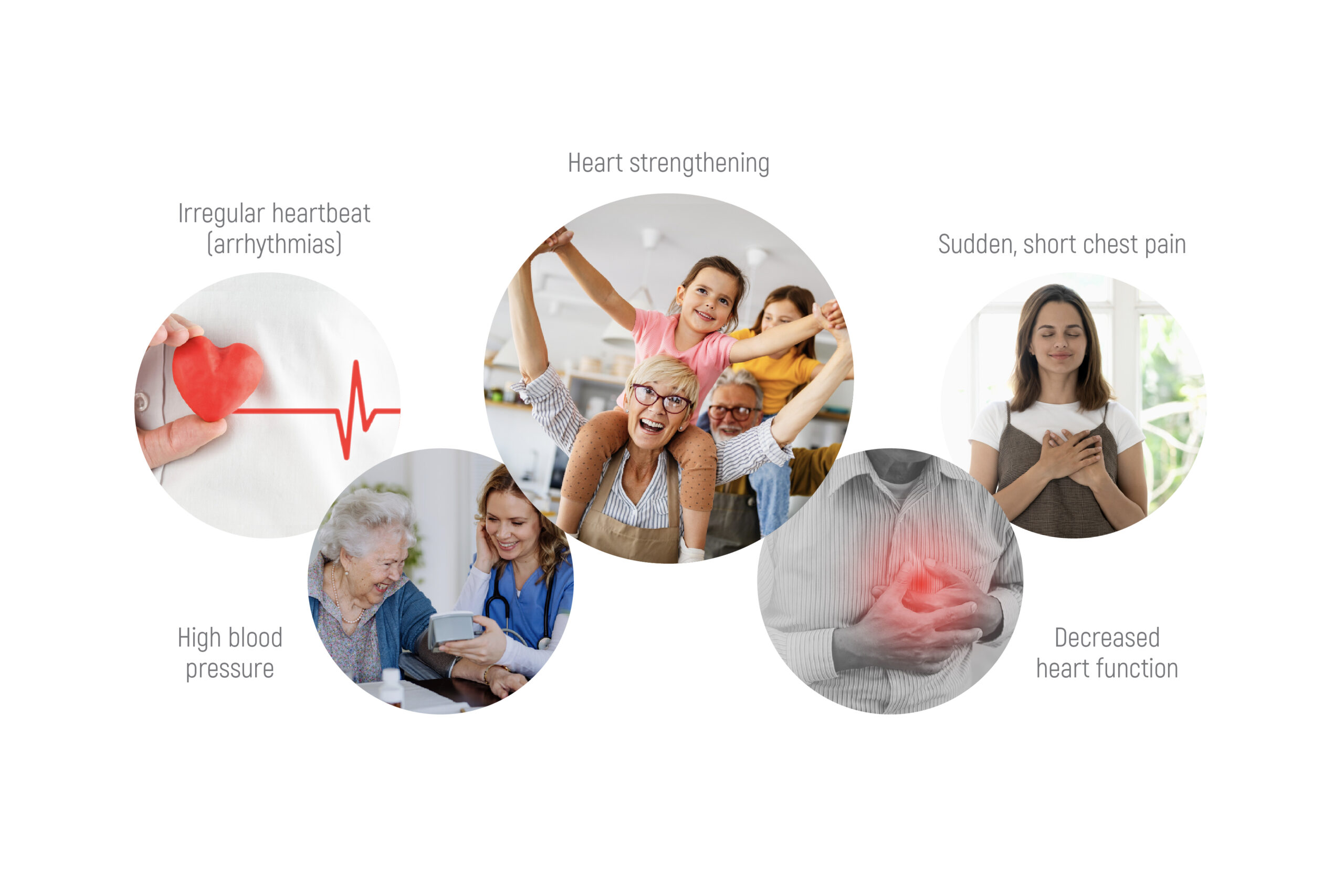
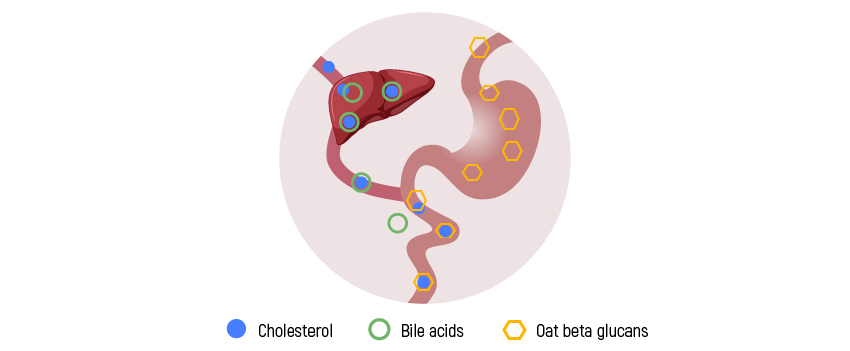
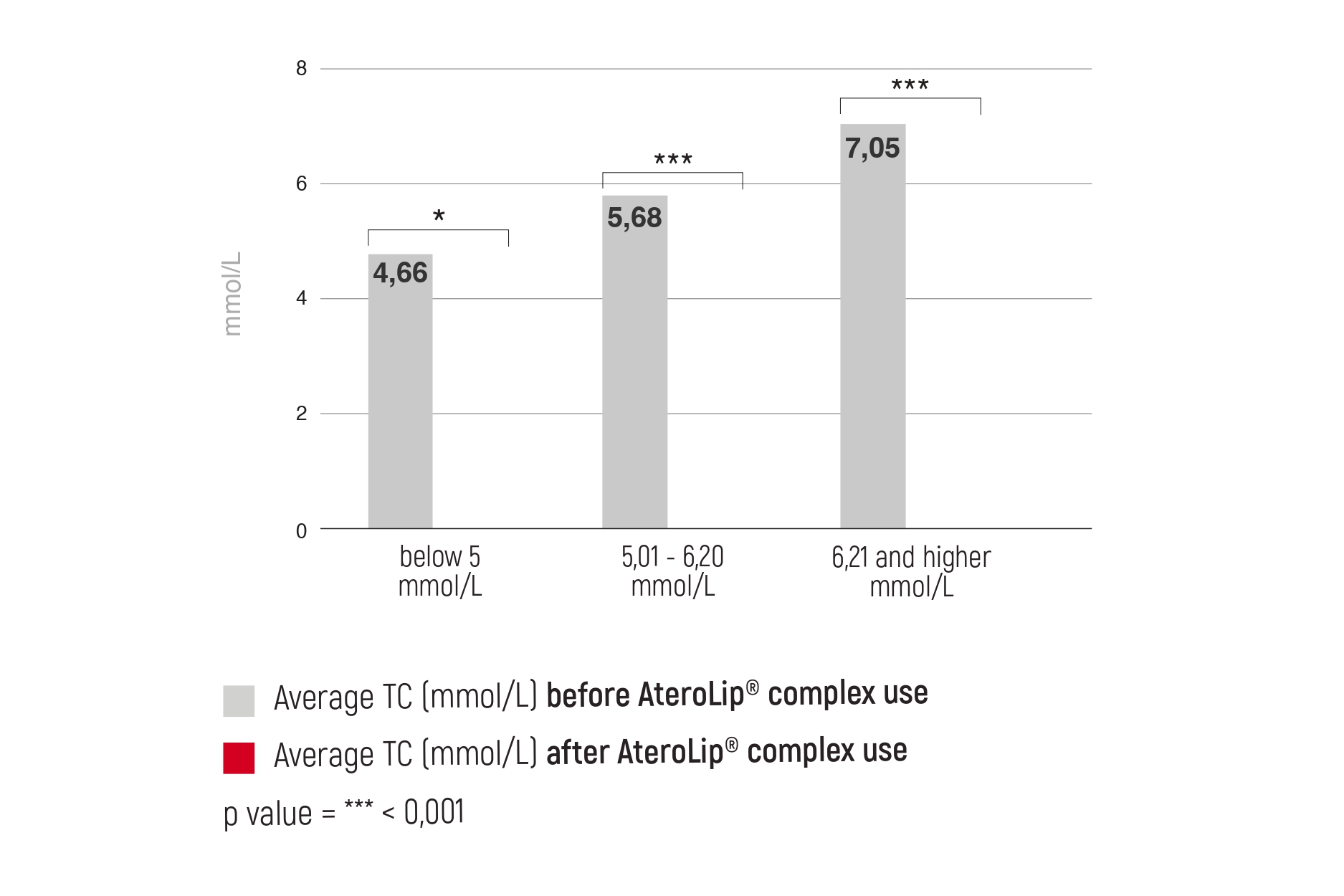
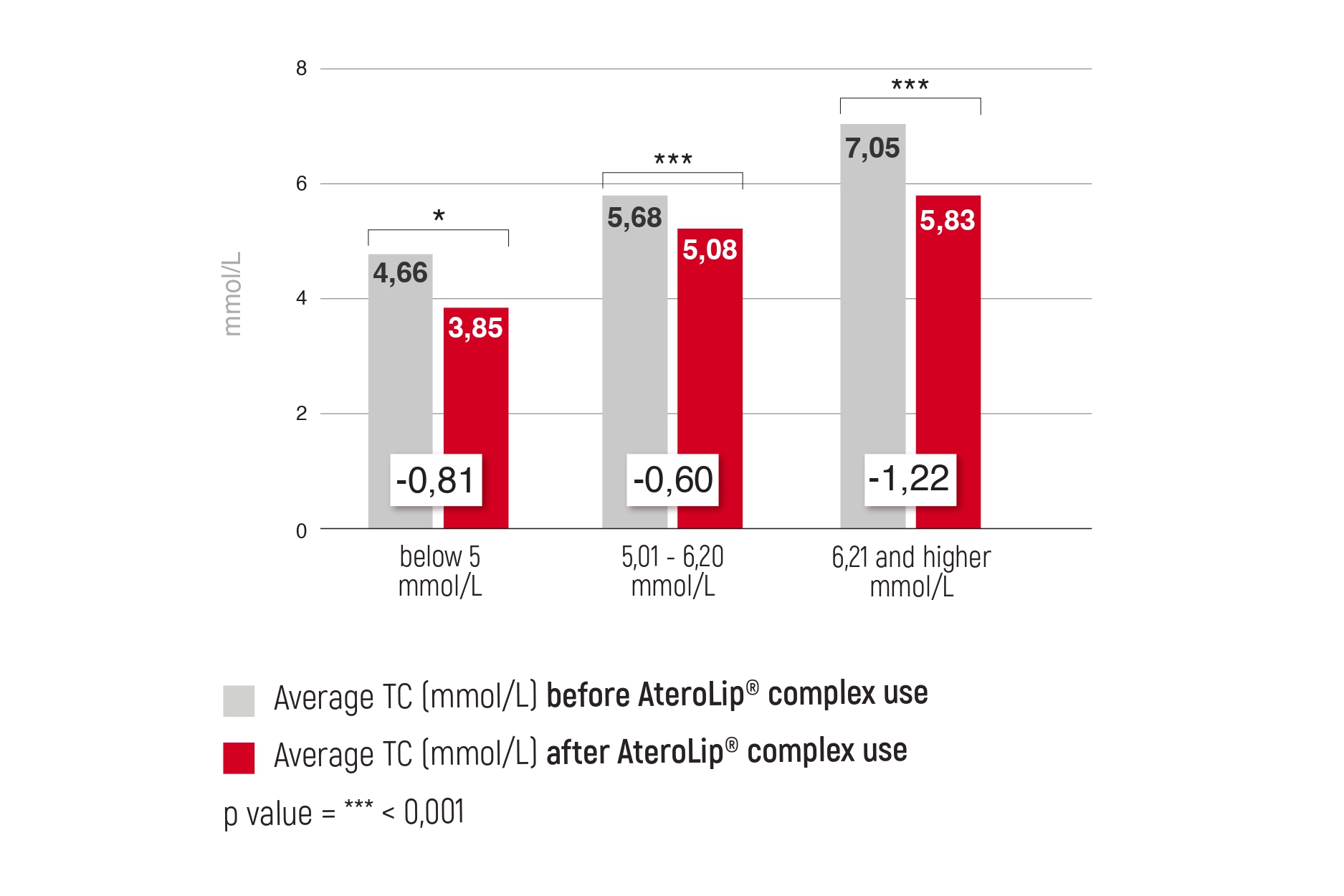
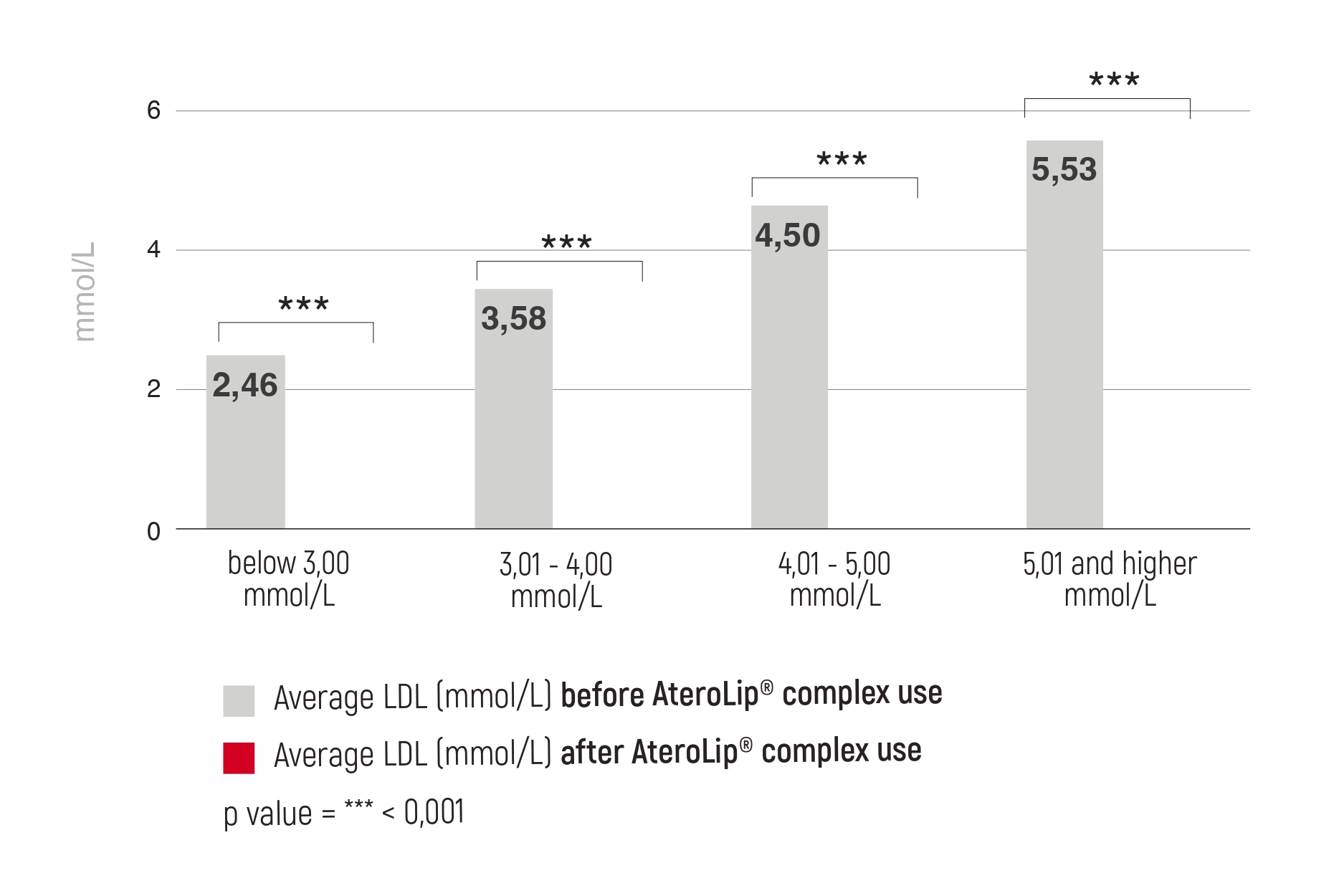
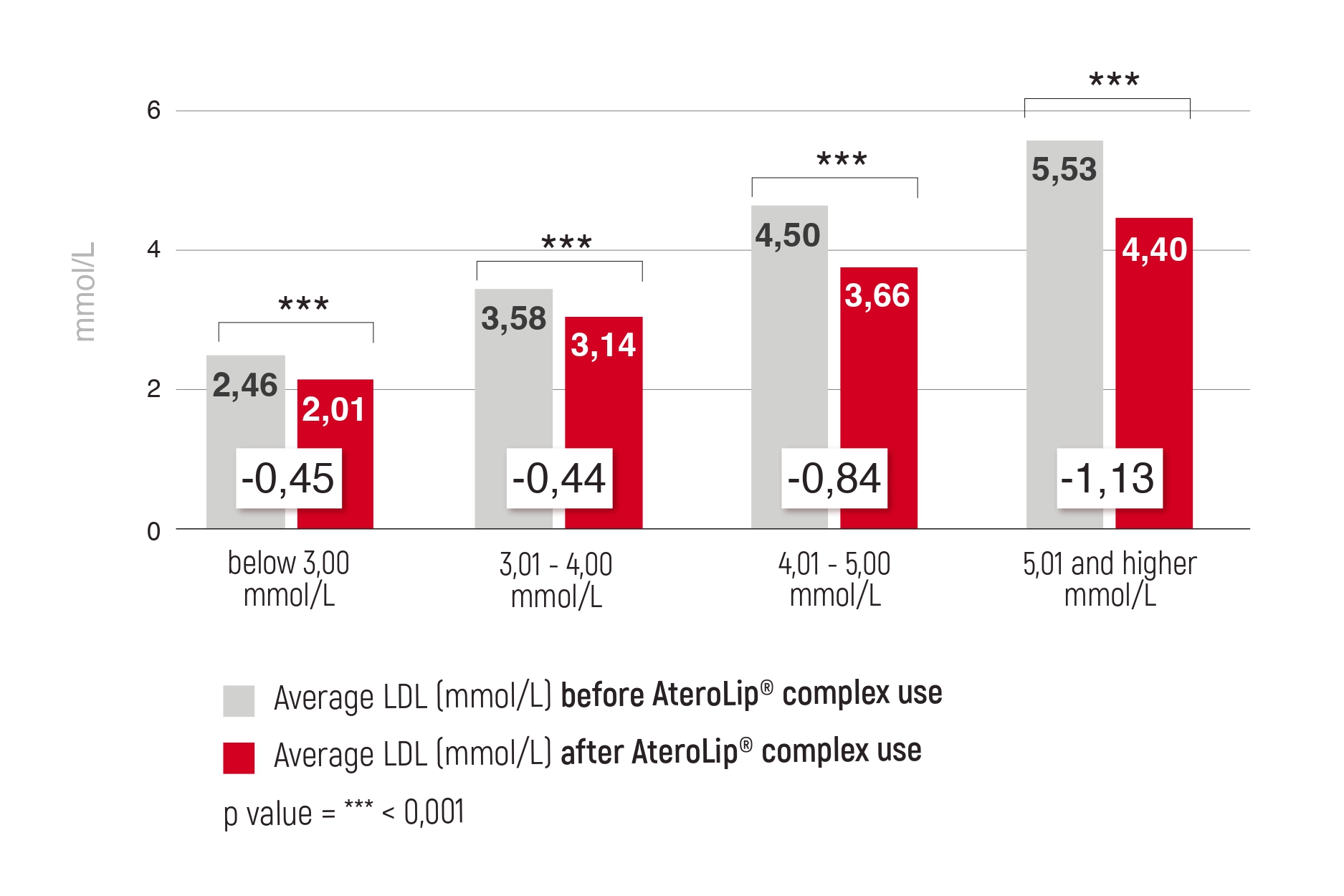
Magnesium is the fourth most common mineral in the human body. It is involved in countless biochemical reactions and enzyme systems, as well as supporting processes such as protein synthesis, cell growth and energy production. Magnesium is needed for nerve function, muscle control, blood pressure regulation and glucose maintenance [1].
Among diabetic patients maintenance of magnesium levels is often neglected , although magnesium deficiency are increasingly common in type 2 diabetes. Oral magnesium is recommended for patients with type 2 diabetes to reduce magnesium deficiency, insulin resistance, oxidative stress levels, and systemic inflammation [2].
1.Romani A. Chapter 3. Magnesium in Health and Disease. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. 2013, 13. Springer. pp. 49–79.
2.Barbagallo M., Dominguex L.J. Magnesium and type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes. Aug 2015, 6(10), pp. 1152-1157.